Chromatography Normal Phase and Reversed Phase
HPLC stands for High-Performance Liquid Chromatography formerly referred to as High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography. Normalreversed-phase chromatography separates molecules by their polarity.

Chemistry Net Liquid Chromatography Hplc Separation Modes Ste Polymer Science Organic Chemistry Books Chemistry Help
HIC acquires an advantage of the hydrophobic.
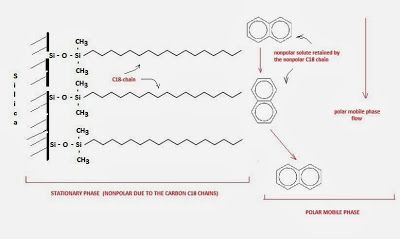
. Cyano Phases For Separation And Extraction. Octadecyl C18 is the most common stationary phase but octyl C8 and butyl C4 are also used in some applications. Normal Phase Liqiuid Chromatography The stationary phase is polar and the mobile phase relatively non-polar.
Ion pair chromatography IPC is an effective reversed-phase liquid chromatographic RPLC technique for separation of organic ions and partly ionized organic analytes. For reversed phase alkyl hydrocarbons are the preferred stationary phase. The technique utilizes the same types of stationary phases and mobile phases as.
Solid phase extraction can be used to isolate. Reversed phase HPLC RP-HPLC has a non-polar stationary phase and an aqueous moderately polar mobile phase. ZORBAX Eclipse PAH 30 or 40 acetonitrile initially to 100 acetonitrile as final solvent.
Quick Overview Of Column Chromatography. The most common stationary phase for column chromatography is silica gel the next most common being alumina. LC-MS offers versatility in the mode of LC operation with reverse-phase liquid chromatography RPLC normal-phase liquid chromatography NPLC hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography HILC.
It may be necessary to cool column to 15 to 20 C for improved resolution. The use of a hydrophobic stationary phase is essentially the reverse of normal phase chromatography since. It is regarded as a type of reversed-phase chromatography and is based on the separation of molecules as per their hydrophobicity.
Because the different constituents of the mixture. Ståhlberg in Encyclopedia of Separation Science 2000 Introduction to Ion Pair Chromatography. A wide range of stationary phases are available in order to perform ion exchange chromatography reversed-phase chromatography RP.
IC - Ion Chromatography. Solid-phase extraction SPE is an extractive technique by which compounds that are dissolved or suspended in a liquid mixture are separated from other compounds in the mixture according to their physical and chemical propertiesAnalytical laboratories use solid phase extraction to concentrate and purify samples for analysis. The stationary phase contains either highly polar normal-phase or highly non-polar reverse-phase functional groups that interact with analytes proportionate to their polarity.
The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent gas or liquid called the mobile phase which carries it through a system a column a capillary tube a plate or a sheet on which a material called the stationary phase is fixed. Steps of Reverse-phase chromatography. General Introduction For Improved Method Development.
The mobile phase is generally an organic solvent such as hexaneheptane. LLC is categorised as - 1Normal Phase Liquid Chromatography 2 Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography 43. Normal Phase HPLC.
The van Deemter equation in chromatography named for Jan van Deemter relates the variance per unit length of a separation column to the linear mobile phase velocity by considering physical kinetic and thermodynamic properties of a separation. Size-exclusion chromatography SEC also known as molecular sieve chromatography is a chromatographic method in which molecules in solution are separated by their size and in some cases molecular weight. Use Of SiliaBond TMA Acetate.
Organic GPC - Size Exclusion. The coupling of chromatography with MS is a well developed chemical analysis strategy dating back from the 1950s. Asahipak NH2P-50 amino.
Effect of pH in reversed-phase chromatography. Gas chromatography GCMS was originally introduced in 1952 when A. The column is prepared with a glass tube applied with solid support like silica gel upon which hydrophobic groups like phenyl octyl butyl are attached.
Cleaning a normal phase silica column 59 Cleaning a reversed-phase polymeric column chromatography59 Method development 61 Method development. Annette C Moser Researchgate. Normal phase chromatography is established on the partition equilibrium between the polar stationary phase and the non-polar mobile phase.
SiO2 HPLC Columns can be used for the separation of strongly hydrophilic compounds in a reversed phase mode with a high organic phase and is particularly suitable for the separation of polar compounds which produce tailing on other company SiO2 columns. The stationary phase or adsorbent in column chromatography is a solid. Columns for the analysis of anions and cations for example in water samples with carbonate or hydroxide eluent.
It facilitates the conversion of cholesterol into bile acids and hence lowers blood cholesterol levels. Thin-layer chromatography TLC is a chromatography technique used to separate non-volatile mixtures. In normal-phase chromatography the least polar.
Martin were trying to develop tandem separation - mass analysis techniques. Stationary phase is an alkylamine bonded to silica. One common stationary phase is a silica which has been surface-modified with RMe 2 SiCl where R is a straight chain alkyl group such as C 18 H 37 or C 8 H 17With such stationary phases retention time is longer for molecules which are less polar while polar.
These properties include pathways within the column diffusion axial and longitudinal and mass transfer kinetics between stationary. Remember that like attracts like. In GC the analytes are eluted from the separation column as a gas and.
Thin-layer chromatography is performed on a sheet of an inert substrate such as glass plastic or aluminium foil which is coated with a thin layer of adsorbent material usually silica gel aluminium oxide alumina or celluloseThis layer of adsorbent is known as the stationary phase. The pH of the mobile phase in reversed-phase HPLC is an important factor it can affect the peak shape as well as the retention time of the molecule as it affects the ionization state of the molecule and therefore. The designations for the reversed phase materials refer to the length of the hydrocarbon chain.
A family of plant guanylate-binding protein-like GTPases controls phase separation and assembly of condensates thereby forming a circuit that regulates transcriptional responses to biotic stress. Where to start Automated method development tools62 Mode Selection 62 Choosing the column and packing dimensions 65 Choosing the stationary phase 66 Method development for reversed-phase. Amine Sorbent For The Separation Of Polar Compounds.
Stationary Phase Usage Notes Most reversed-phase columns 5 methanol or acetonitrile initially and 100 methanol or acetonitrile as the final solvent. Asahipak ODP-50 C18 RSpak DE DM DS RP RSpak NN JJ multi-mode RPIEC ODP2 columns. It helps in the synthesis and metabolism of tyrosine folic acid and tryptophan hydroxylation of glycine proline lysine carnitine and catecholamine.
Reversed-phase chromatography is a technique using alkyl chains covalently bonded to the stationary phase particles in order to create a hydrophobic stationary phase which has a stronger affinity for hydrophobic or less polar compounds. Cellulose powder has often been used in the past. SiO2 liquid chromatography column is suitable for most normal phase chromatography.
The elution peak of monodisperse packing is higher and narrower the separation is better the elution is more concentrated the sample concentration is higher the elution volume. Steps of a reversed-phase chromatography separation. Typically when an aqueous solution is used to.
It is usually applied to large molecules or macromolecular complexes such as proteins and industrial polymers. TFA Removal Using SiliaPrep. How NormalReversed-Phase Chromatography Works.
The body requires vitamin C for normal physiological functions. In chemical analysis chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components.

The History And Development Of Reversed Phase Chromatography Problem And Solution Gas Chromatography Solutions

What Is Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography Lc Hplc Chemistry Net Chemistry Reverse Steroids Side Effects

Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography Animation Rplc University Of Minnesota Reverse Animation

Normal Phase Liquid Chromatography Lc Hplc Chemistry Net Chemistry Education Liquid

Normal And Reversed Phase Thin Layer Chromatography Of Green Leaf Extracts Journal Of Chemi Thin Layer Chromatography Dimensional Analysis Chemical Education

Comments
Post a Comment